Fuel Cell

Fuel Cell Overview
- It is an energy conversion device that converts the chemical energy of a fuel directly into electrical energy through electrochemical reactions. Unlike batteries, electricity can be produced without recharging as long as the fuel is supplied, and heat generated during the reaction can be used for hot water production and used for heating.
-
- H2+1/2O2 → H2O+electricity
- New technology where the product is electricity and pure water has a power generation efficiency of 30~40% and thermal efficiency of 40%, with a total efficiency of 70~80%.
Fuel cell power generation principle
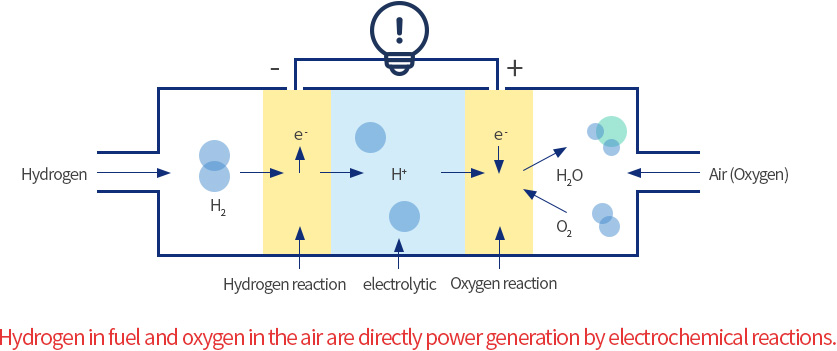
- 1. Hydrogen supplied to the fuel pole is separated by hydrogen ion and electrons.
- 2. Hydrogen ion moves through the electrolyte layer to the air pole, and electrons move through the external circuit to the air pole.
- 3. Oxygen and hydrogen ions meet in the air pole to produce a reaction product (pure water).
- >> Final reaction is that hydrogen and oxygen combined to produce electricity, water and heat
Fuel Cell Characteristics
- 1. High efficiency : 40~60% power generation efficiency, 80~85% overall efficiency(including waste heat and etc.)
- 2. Energy savings : 25~50% energy savings when using fuel cells
- 3. Environmental friendly energy(Clean energy) : There is little emissions of SOx(sulfur oxide) and NOx(nitrous oxide). Co2 is less than half of the conventional way. There is little noise and vibration.
- 4. Module structure : Small area needed. Easy to install and expand. Easy transport. Reduced power plant construction period.
- 5. Distributed Power : Easy urban installation for pollution-free and small footprint. Reducing the cost of power transmission facilities
- 6. Cogeneration : Heating, Hot Water, Cooling and Heating Using Arrangement
- 7. Various fuels : LNG, LPG, methanol, Naphtha, coal gas, hard oil, etc.
- 8. Autonomy of Development Scale
Fuel Cell block diagram
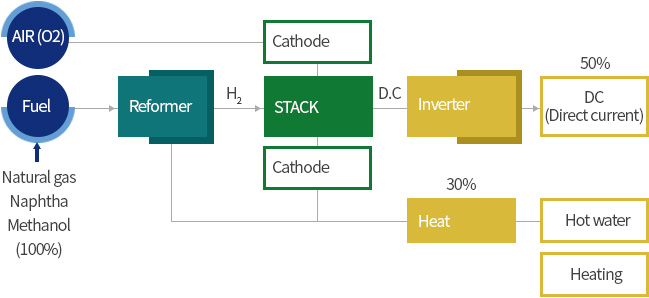
- Reformer : A device that converts fossil fuels into hydrogen fuel
- Stack : A power plant that generates electricity from hydrogen
- Inverter : DC(direct current) electricity is converted to AC(alternative current) electricity
- BOP(Balance of Plant) : A device that recovers waste heat and supplies hot water or heating